
Key Takeaways
► Drones rely on many integrated systems, so each component requires targeted and reliable testing.► Precise positioning and sensor accuracy ensure safe navigation and consistent obstacle avoidance.
► Battery testing protects safety, endurance and overall energy efficiency across all drone sizes.
► Motor and camera validation ensure stable flight performance and high-quality imaging.
► Consumer and defense drones require different testing depth, but both benefit from automated and repeatable validation.
Once seen as futuristic ideas in science fiction, drones have become practical and tools across many industries. Today they support defense applications, inventory management, site scouting, filmmaking and consumer entertainment.
Nearly every industry now benefits from drones, and the one thing they all have in common is that each drone has dozens of capabilities that need to work.
First of All: Definition of UAV and Drone
A UAV is an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and refers strictly to the aircraft operating without an onboard pilot.
A drone is the broader everyday term that includes the UAV plus all supporting elements such as remote control, sensors, communication links and automated flight capabilities.
Testing a Drone: Where to Begin
Drone testing does not follow a single starting point because each platform integrates many specialized electronic systems and sensing technologies. Depending on the size and sophistication of the drone there are multiple boards with sensors, CPUs, cameras, GNSS trackers, electric motors, batteries, collision avoidance systems, gyroscope stabilization and more. Manufacturers and engineering teams need to validate each of these components before setting flight.
How are Drones Tested from an Engineering Perspective
Engineers divide the testing process into three stages:
-
Development Testing
This involves component-level testing of different features to ensure they meet the end customer’s requirements. -
Qualification Testing
This stage ensures the regulatory requirements are mt, including stress and environmental tests. The most challenging aspects are ultimate loading scenarios and endurance testing. - Acceptance Testing
This is the end-of-line testing performed on every part during production.
Position & Collision Avoidance Validation
Drones must always know exactly where they can fly safely. Reliable location information helps them stay stable, avoid obstacles and return home when needed. Regardless of the assigned task, position and navigation validation ensures accurate sensing and correct responses in real conditions Collision avoidance system tests are performed to detect both moving and stationary objects. This includes the performance of cameras, infrared, ultrasonic, stereo vision, and multi-sensor fusion in varied lighting and environmental conditions. That said, in the real world, accidents happen. Collision tolerance tests are also a must to understand resilience. Metrics such as Modified Acceleration Severity Index (MASI) or Maximum Delta‑V can quantify impact severity.
GNSS testing for UAVs
Many drones depend on satellite based GNSS systems for precise navigation and stable positioning. They often combine signals from GPS (United States) and GLONASS (Russia) signals to improve coverage and accuracy.
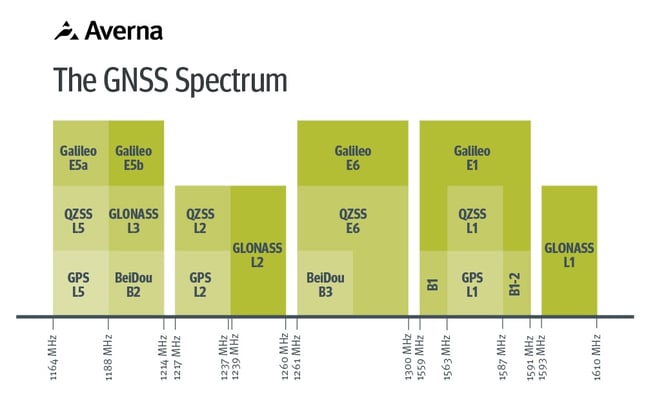
Depending on the application, positioning accuracy is often critical for stable flight, safe navigation and reliable mission outcomes. Hobby drones may not require perfection, but drones used for mapping or military environments need the highest precision.
To test this properly, engineers use tools that can capture the full GNSS spectrum using RF test equipment. A platform such as the RP-6500 captures the full GNSS spectrum including natural distortions and interference. These recordings can be replayed to verify how the drone behaves in authentic conditions while keeping costs under control.
Accurate positioning also supports convenience and safety features. For example, return to home functions only work reliably when the drone knows where it is!
Sensor fusion and obstacle detection testing
Reliable operation and collision avoidance depend on accurate radio frequency performance, precise radar-based sensing and high quality real-time sensor fusion. High end drones detect and avoid obstacles by generating 3D maps using technologies such as:
• LiDAR
• Machine vision
• Ultrasound
• Infrared
Battery Testing for Battery Safety and Endurance
Drone batteries must match the size, weight, safety and power delivery requirements of the platform to ensure stable performance and reliable endurance. For battery testing, engineers focus on:
• Overcharging and forced discharging
• Battery cycling
• High and low temperature verification
• Temperature cycling
• Short circuit testing, resistance testing and insulation testing
• BMS functional verification and validation
• Optical inspection for very small defects
• Mechanical shock testing, leakage testing and vibration integration
Averna’s Batterie Inspektor™ platform is an excellent example of an all-in-one tool for flexible battery testing, regardless of the application.
Production Testing for Drone Battery Packs
During manufacturing there is a fully automated cell sorting and inspection process at the micron level (µm) using automated visual inspection systems. This is followed by module and battery pack testing, including charge and discharge cycles, open circuit voltage, AC internal resistance, DC internal resistance, high voltage insulation and leak testing as well as BMS application tests. This ensures anything less than perfect never makes it out in the world.
Electric Motor and Propulsion Testing
Electric motor testing ensures stable propulsion, efficient power delivery and consistent thrust performance in UAVs. The principles mirror those used in electric vehicle (EV) motor validation, where consistent torque behavior, controlled acceleration and efficient energy use are central. These same foundations guide testing for drone scale propulsion systems.
Verifying Motor Behavior across Flight Conditions
Testing the motor of a drone applies the principles of EV-motor testing to smaller, faster rotating propulsion units. Engineers evaluate high inrush current during acceleration, monitor vibration and mechanical stability, analyze high revolution coupling and measure potential energy loss. These focused tests confirm safe, efficient and consistent propulsion performance across all expected flight scenarios.
Camera Systems and Optical Alignment
Camera systems play a central role in modern UAV performance, especially for high quality aerial imaging, inspection workflows and navigation support. Reliable imaging requires precise optical alignment, accurate sensor calibration and controlled assembly that ensures consistent output at high volumes. These capabilities are supported by advanced vision inspection techniques and specialized active alignment processes that help maintain the highest image quality in every flight scenario.
Active Alignment for High-Precision Aerial Imaging
Many high-resolution aerial shots are captured using drones and they depend on very high quality cameras. For fast and accurate camera and optical device assembly the active alignment process is the most effective approach. This process includes the preparation stage, controlled glue application, precise component alignment, curing and final validation. This ensures consistent and flawless imaging performance.

Final Manufacturing Validation: EOL Testing for Drones
Before leaving the production line, every drone must pass complete end-of-line (EOL) testing to verify full functionality and production quality. Under controlled and repeatable conditions, all essential functions are verified: navigation, sensing, RF links, motor control, battery behavior and camera systems.
Drone Testing Requirements: Consumer vs. Aerospace & Defense
Drone testing requirements vary widely depending on the operating environment. UAVs built for the consumer electronics sector need affordability, imaging performance and consistent behavior at high production volumes, while aerospace and defense products must deliver certified performance in harsh and unpredictable conditions. With this in mind, consumer electronics test systems and aerospace & defense test equipment will look very different. Each have specific yet different requirements for validation, including functional testing, environmental testing and RF and GNSS performance. That said, both benefit from structured and scalable strategies supported by modern automated test solutions.
When Automated Test Systems Make the Difference
Automated test solutions simplify and accelerate UAV validation. With the right design, they can test all the requirements each unique drone requires and delivers full traceability. They produce structured data logs for audits and compliance reviews while ensuring complete repeatability across all tests.
Work with Test Engineering Experts in UAV Validation
Averna’s team supports UAV manufacturers with precise, automated platforms tailored to complex RF, GNSS, vision, battery, and propulsion testing. Reach out to discuss a validation strategy that scales with your requirements.
You may also be interested in…

Looking to automated PCBA validation? Look at the benefits it brings!
Get in touch with our experts or navigate through our resource center.
